do you know how car engine works?(automobile engineering)
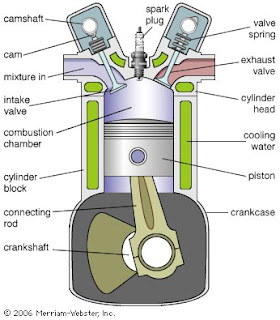
First things , the car engine is an internal combustion engine, of which there are a number of various types including diesel engine , gasoline engine , rotary engine and engine two times . The internal combustion engine works with the basic premise of injecting a small amount of high-energy fuel, eg gasoline or diesel in a small closed space, lighting and creating a massive amount of energy as a gas in expansion. The trick of the internal combustion engine is removed is the accusation of explosions like this hundreds of times for one minute and management to harness the energy that is thus created. Almost all cars use four-stroke cycle combustion to convert fuel into motion, the four strokes being - intake, compression, combustion and exhaust. In the beginning of the cycle the piston starts on top, once the intake valve opens, the piston moves downward, letting the engine take in a cylinder filled with air which also injects a drop Petrol. The piston moves back ...