Fundamentals of Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning (course ) 2
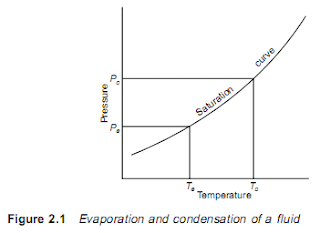
2.1 Basic vapour compression cycle A liquid boils and condenses – the change between the liquid and gaseous states – at a temperature which depends on its pressure, within the limits of its freezing point and critical temperature. In boiling it must obtain the latent heat of evaporation and in condensing the latent heat must be given up again. The basic refrigeration cycle (Figure 2.1) makes use of the boiling and condensing of a working fluid at different temperatures and, therefore, at different pressures. Heat is put into the fluid at the lower temperature and pressure and provides the latent heat to make it boil and change to a vapour. This vapour is then mechanically compressed to a higher pressure and a corresponding saturation temperature at which its latent heat can be rejected so that it changes back to a liquid. The total cooling effect will be the heat transferred to the working fluid in the boiling or evaporating vessel, i.e. the change in enthalpies b...
