Internal Combustion Engines Components 2 (automobile engineering)
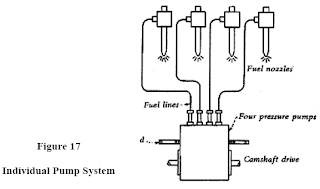
in the previous section we had discuss : Classification of Internal Combustion Engines and Engine Components (Course) that we had discussed in : -Classification of Internal Combustion Engines -Internal Combustion Engine Components lets begin our section which we will discuss : -Describe individual pump, distributor, and common rail fuel injection systems for a diesel engine. -Explain the purpose and describe the operation of superchargers and turbochargers - Describe the cooling systems, function operation, inspection, and service. SECTION 2 Objective 3 Describe individual pump, distributor, and common rail fuel injection systems for a diesel engine. THE FUEL INJECTOR The diesel engine, unlike some gasoline engines, does not use a carburetor to mix the fuel and air nor does it use a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture. Instead, the diesel uses an injection system to spray the fuel into the engine cylinder. The fuel...